mymesh.primitives.Extrude#
- mymesh.primitives.Extrude(m, distance, step, axis=2, twist=0, twist_center=None, ElemType=None)[source]#
Extrude a 2D mesh to a 3D surface or volume
- Parameters:
m (mymesh.mesh) – mesh object of 2D line mesh (m.Type=’line’) or 2D surface mesh (m.Type=’surf’)
distance (scalar) – Extrusion distance
step (scalar) – Step size in the extrusion direction
axis (int, optional) – Extrusion axis, either 0 (x), 1 (y), or 2 (z), by default 2
twist (float, optional) – Amount to twist the initial geometry (in radians) over the course of the extrusion, by default 0.
twist_center (array_like, optional) – Center of rotation for twisting. If None is provided, the center of the initial geometry will be used.
ElemType (str, optional) – Specify the element type of the extruded mesh. If m.Type=’line’, this can be None or ‘tri’ or if m.Type=’surf’, this can be None or ‘tet’. If ‘tri’ or ‘tet’, the mesh will be converted to a purely triangular/ tetrahedral mesh, otherwise it will follow from the input mesh (input line meshes will get quadrilateral elements, input surf meshes could get hexahedral, or wedge meshes). By default, None.
- Returns:
extruded – Mesh object containing the extruded mesh.
- Return type:
Note
Due to the ability to unpack the mesh object to NodeCoords and NodeConn, the NodeCoords and NodeConn array can be returned directly (instead of the mesh object) by running:
NodeCoords, NodeConn = primitives.Extrude(...)Examples
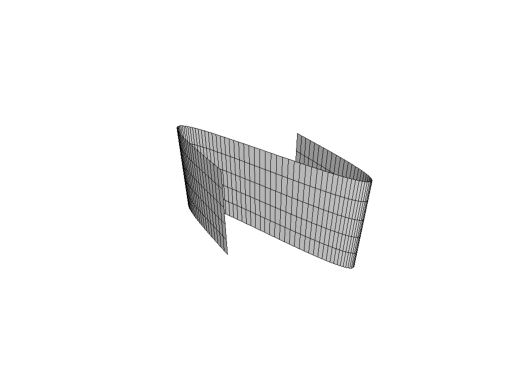
x = np.linspace(0,1,100) y = np.sin(2*np.pi*x) coordinates = np.column_stack([x, y, np.zeros(len(x))]) connectivity = np.column_stack([np.arange(len(x)-1), np.arange(len(x)-1)+1]) line = mesh(coordinates, connectivity) extruded = primitives.Extrude(line, 1, 0.2) extruded.plot(bgcolor='w', show_edges=True)